Abstract: The aim of this article is to contextualise universities historically within capitalism and to analyse academic labour and the deployment of digital media theoretically and critically. It argues that the post-war expansion of the university can be considered as medium and outcome of informational capitalism and as a dialectical development of social achievement and advanced commodification. The article strives to identify the class position of academic workers, introduces the distinction between academic work and labour, discusses the connection between academic, information and cultural work, and suggests a broad definition of university labour. It presents a theoretical model of working conditions that helps to systematically analyse the academic labour process and to provide an overview of working conditions at universities. The paper furthermore argues for the need to consider the development of education technologies as a dialectics of continuity and discontinuity, discusses the changing nature of the forces and relations of production, and the impact on the working conditions of academics in the digital university. Based on Erik Olin Wright's inclusive approach of social transformation, the article concludes with the need to bring together anarchist, social democratic and revolutionary strategies for establishing a socialist university in a commons-based information society.
Keywords: Critical Social Theory, Academic Labour, Digital Media, Universities, Knowledge Workers, Digital Labour, Informational Capitalism, Working Conditions, Struggles
Acknowledgement: A shorter version of this article has been published in Critical Sociology: OnlineFirst, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1177/0896920517735669
Universities are often seen as intellectual spaces and communities of scholars, rather than workplaces. At least historically, university lecturers and professors have been considered as being engaged in a higher vocation, similar to writing poetry (Harvie 2006, 9). The activities of academics have been understood as a high mission, rather than labour, and academics as citizens, rather than workers. This argument is often used to dismiss the political concerns of academic workers (Gulli 2009, 15).
Academic labour studies is an interdisciplinary field in the intersection of subject areas such as education, management, policy studies, cultural studies and sociology. The field is constantly growing, reflected in an expanding literature reporting about the changes in the working conditions of academics. One of the aims of academic labour studies is to bring down university work from its high mission.
However, Winn (2015, 4, 10) argues that the academic labour studies literature tends to be essayistic in style, hardly engaging on a theoretical level, but criticising neoliberal developments, romanticising the 'golden age' of universities and wanting to restore Fordist configurations. This article strives to move beyond this critique by focusing on a critical social theory approach, contextualising universities historically within capitalism and analysing academic labour theoretically.
While teaching and research at universities becomes more virtual and digital (for example: online research and digital methods, virtual learning environments, Massive Open Online Courses), several authors (Noble 1998; Gregg 2013; Lupton 2014; Poritz and Rees 2017) have suggested that the deployment of digital media has an impact on the working conditions of academics; to name but a few, the blurring of working space and other spaces of human life, always on cultures, and digital surveillance.
Therefore, this paper focuses on the following areas by moving from the abstract to the concrete level:
- Historical context: universities and academic labour
- Academic labour: theoretical analysis of forms, concepts and conditions
- Digital media: impacts on universities and academic labour
I address these points based on a critical social theory approach. In doing so, I engage with the history and context of universities in the next section. Section two deals with the forms and concepts of academic labour and provides a systematic analysis of working conditions at higher education institutions. The impact of new information and communication technologies on academic labour is outlined in section three. The article concludes with a summary and discusses political potentials and alternatives. While occasional references are made to other areas such as the US and Continental Europe, this article mainly focuses on the UK.
1. Historical Context: Universities and Academic Labour in Informational Capitalism
Older universities such as the ones in Oxford and Cambridge had been founded before the modern British state was created. Considered historically, British universities have been understood as communities of scholars pursuing knowledge and advancing learning. The medieval idea was that academics should organise themselves, where collegiality plays an important role (Callinicos 2006, 21). This idea is still reflected in their current legal form and so most of them are today independent corporate institutions with charitable status. British universities are not state organisations as they are in many other European countries such as Germany and Italy. Nor can their employees be considered as civil servants. Since UK universities were legally never state organisations, but rather independent, care must be taken in using the term 'privatisation', although the UK government has recently implemented new legislations that provides universities the freedom to change their corporate form in order to better access private investment (McGettigan 2013, 128). Outsourcing several tasks and creating joint ventures with the private sector are further strategies of universities to undermine their charity status (for further information on this, see: McGettigan 2013, 128).
The higher education landscape has changed in the last decades. One of the most obvious changes is the expansion in terms of providers, student population and university staff in absolute numbers. Considering Scotland as an example, 232,570 (part- and full-time, under- and postgraduate, national and international) students were enrolled in the academic year 2014/2015. In contrast, 223,530 people studied in Scotland in 2006/2007 and 163,519 people in 1996/1997. This is an increase of 36.7 per cent from 1996 to 2006 and a further increase of 4.0 per cent from 2006 to 2014. One of the main drivers of this expansion is the internationalisation of the higher education sector. 50,015 international students (other European Union and non-European Union students) study at one of the 19 higher education institutions in Scotland. Considering the postgraduates separately, 40.7 per cent of the students come from outside the UK. 19,250 (part- and full-time) academics, 10,515 academic atypical staff and 23,650 non-academic staff are employed at Scottish universities. Almost two-thirds (64.9 per cent) of them work in the major cities Edinburgh and Glasgow (all data for the academic year 2014/2015: Higher Education Statistics Agency 2016).
One of the crucial questions is how to assess the expansion of the universities. According to Callinicos (2006, 5), there are two main competing ways of interpretation:
1. One way might be to criticise those developments based on the argument that an expansion of the university necessarily brings down the quality of higher education. The expansion leads to quantity instead of quality, worsened staff-student ratio and a devaluation of the university degree in general. This line of argument is often accompanied with the idea that universities should remain a privilege of a minority being educated at elite universities. This position considers the expansion of universities as a negative development and is traditionally linked to conservative politics.
Indeed, the staff-student ratio has decreased (Higher Education Statistics Agency 2016) and the workload and time pressure for academic staff have increased (University and College Union 2016a, 18-19) in the last decades that might also have a harmful effect on the quality of research and teaching at universities in the UK. But the question remains if these developments are necessarily an outcome of the expansion of universities or rather its political and economic conditions. One could imagine expanding higher education with the provision of the necessary resources and thereby promoting real social inclusion. The critique on the vanishing quality of higher education entails some true elements, but it remains fragile in the analysis of the causes and the suggested solutions. Romanticising the past, arguing for higher education as a privilege for the few and defending elite universities remains a deeply conservative and reactionary ideology.
2. Another position might be that the expansion of the university widens access for people from poorer backgrounds, women and ethnic minorities and thereby provides inclusion, equality of opportunities and social justice. Education is considered as a route out of poverty and disadvantage and to build a more socially just society. Traditionally linked to labour politics, the expansion of the university is rather considered as a positive development.
The expansion of the university and the widening of its access for students and academics from poorer backgrounds, women and ethnic minorities can be considered as an important achievement and social advancement of the last century and was partly the outcome of class struggles, women movements and civil right movements (Dyer-Witheford 2005, 80). In addition, the expansion of higher education also led to a broader politicisation across social strata and resulted in student movements at several advanced industrialised societies such as Germany and France in the late 1960s. These developments can be considered to be on the subjective level, because human actors, agencies and social groups stood up, raised their voice and fought in order to change university structures and society to the better. It is the impact of humans on society.
Capitalism has changed from a Fordist to a post-Fordist accumulation regime and from a Keynesian to a neoliberal mode of regulation (Jessop 2002). Even more than Fordism, informational capitalism requires and rests on trained and skilled workers such as managers, technocrats and scientists being able to plan, manage and operate the sophisticated production process. The expanded university provides such a workforce by being an ideal place for employability and to train workers for the post-Fordist market (Dyer-Witheford 2005, 71). The neoliberal university provides the workforce for corporations at no costs as higher education is funded by the state and/or paid individually through tuition fees. Capital thereby expropriates the commons.
Besides the tight subordination of teaching to economic needs, research has been changing in the post-Fordist area as well. Much more research is necessary since the spheres of production, circulation and consumption have become more complex. While bigger companies tended to have their own research laboratories, the post-Fordist accumulation regime requires research at a scale that urges companies to outsource research to universities in order to reduce costs (Callinicos 2006, 13). New joint ventures between universities and the private sector have emerged to the logic of international competition and profit. The costs and risks of research have thereby been socialised, while the benefits of innovation privatised (Dyer-Witheford 2005, 76; Noble 1998). Because of the changing nature of both teaching and research in the neoliberal era, Dyer-Witheford (2005, 76) claims that 'capital becomes more intellectual; universities become more industrial'. Academic research has become crucial for post-Fordist accumulation (Dyer-Witheford 2011, 279).
In summary, the post-war expansion of the university can be considered as medium and outcome of the informational capitalism. While research laboratories contributed to bring forward information technologies and techno-scientific innovations that helped to develop a knowledge-based economy (medium), informational capitalism requires a highly trained and skilled workforce being provided by the neoliberal university (outcome).
As part of the neoliberal project, the state has gradually pulled back and a radical privatisation, liberalisation and deregulation of the market have been pushed forward in order to stay internationally competitive. It was primarily the neoliberal ideology of Margaret Thatcher era in the UK and Ronald Reagon epoch in US in the 1980s, starting a process of massive cuts in social services and a reduction in tax for business and simultaneously providing subsidies, which had an enormous impact on working conditions including the introduction of flexible working hours, lowering wage level, increased workloads, less job security, etc. These developments have not only been taken place in the private sector, but also in public institutions such as universities. With the rise of neoliberalism, a 'new manageralism' (Deem, Hillyard and Reed 2007) was implemented in the public sector, affecting both students and staff at higher education institutions. Today's universities have thus to be considered in the context of capitalism's transition from a Fordist to a post-Fordist accumulation regime and a Keynesian to a neoliberal mode of regulation.
As I argued above, the widened access of universities is the historical success of social struggles by humans on a subjective level. Simultaneously, capitalism rests on the expansion of universities as it requires advanced research and a high skilled workforce under neoliberal and post-Fordist conditions. These developments are objective in contrast, because social structures enable and constrain individual actions. In order to answer the question if the expansion of the university can be considered as a positive development that promotes social justice, one has to take into account not only the subjective, but also the objective level and the neoliberal and post-Fordist context. In principal, capital does not mind about the social background of people, as long as they conduct valuable research and can be exploited as trained and skilled workforce. 'The impassable limit of campus identity politics is marked by its recuperation to cognitive capital's drive for a wider recruitment of social intelligence. An official academic credo of multiculturalism and gender-equity opens the way to more comprehensive and efficient commodification of intellectual labour-power.' (Dyer-Witheford 2005, 80) The expansion of the university is neither positive, nor negative, but a contradictory development by widening access for both subordinate groups and capital's interests. In analogy to Horkheimer and Adorno's (1969) understanding of the enlightenment as a dialectic process of progress and regress, liberty and barbarism, the university expansion can also be understood as a dialectic development of progress and regress, social achievement and advanced commodification.
Because the two main competing ways of interpreting the expansion of the university are flawed, a third option is introduced here:
3. Terranova (2004) argues that 'the debate seems to be stuck in the false opposition between the static, sheltered ivory tower and the dynamic, democratic market'. As a result, we need a socialist expansion of the university that provides the necessary material resources in order to ensure teaching and research at a high quality on the one hand and a political and economic context in order to widen access to education in general and higher education in particular for all social groups without interferences of capital's interests of cheap labour power and industrial research on the other. 'Our understanding of the mode of knowledge production in higher education and its conceived role and purpose in public life over the last century must start from a categorical understanding of capitalism and the historical mode of production that reproduces the university'. (Winn 2015, 11) The struggle for better universities can thus not be separated from the struggles against capitalism (Callinicos 2006, 7; Gulli 2009).
2. Academic Labour
In the following, I deal with the forms and concepts of academic labour, before a systematic analysis of the working conditions at universities is provided.
2.1. Forms and Concepts of Academic Labour
The discussion about academic labour brings up the question if academic workers are part of the proletariat, create value and are exploited in capitalist societies. These questions are important theoretical ones in order to be able to situate academics in a class concept appropriately. Identifying the class position of academic workers is important for political reasons: to create relationships and solidarities and to understand class struggles.
In the introduction to the English version of 'Capital: Volume Two', Mandel argues that Marx used a broad concept of the proletariat that includes all workers who have to sell their labour power. 'The defining structural characteristic of the proletariat in Marx's analysis of capitalism is the socio-economic compulsion to sell one's labour-power. Included in the proletariat, then, are not only manual industrial workers, but all unproductive wage-labourers who are subject to the same fundamental constraints: non-ownership of means of production; lack of direct access to the means of livelihood [...]; insufficient money to purchase the means of livelihood without more or less continuous sale of labour-power.' (Mandel 1992, 47) If we accept such a broad understanding and reject the narrow definition of the proletariat as constituted only of productive workers, academics can be considered as part of the proletariat, independently if they create value and are productive or unproductive labourers.
In order to answer the question of value creation and exploitation of academics, it makes sense to have a look at how state theorists analyse the role of public organisations and civil service employees in general. In reference to Yaffe and Offe, Wright (1978, 155-156) argues that 'state production is itself not production for the market and thus the state does not accumulate capital out of any realized profits from its own production. Most state expenditure therefore do not directly produce surplus value'. In 'Class Counts', he furthermore claims that state employees' 'wages are largely paid out of taxes, and thus they have a different relationship to private profits and public taxation than employees of capitalist firms' (Wright 1997, 462). If we follow this line of reasoning, one can say that in comparison to workers in other sectors such as engineers in a private company, academics are normally not employed and therefore not directly exploited by capitalists. Many academics are employed by the state or a charity not producing profit and thus cannot be regarded as capitalist enterprises. For schools, which are in this context comparable to universities, Harris (1982, 57) argues that teachers 'are employed by the State and they are paid out of revenue - they are therefore unproductive labourers'. Teachers are 'outside of the valorisation process, and they do not directly produce surplus value' (Ibid., 128). At universities, there is no such a relationship between workers on the one hand and an owner of productive forces (i.e. capitalist) on the other. Operations such as investing in the stock market, creating joint ventures with the private sector, outsourcing several tasks, minimizing democratic structures, implementing new management methods, etc. let appear higher education institutions very similar to private companies, but the main difference is that universities are owned by the public and not individuals. The property relations between private companies and universities differ.
Marx describes land and nature as the objects of labour, but one can argue that information and knowledge might also serve as objects of labour in the mode of production. Marx himself draws this possibility in the 'Grundrisse'. The technological development of the productive forces causes a rising importance of science, information and general social knowledge in the capitalist process of production. Knowledge becomes a direct force of production. In this context, Marx (1997) has raised the notion of the 'general intellect'.
It can be stated that capitalism has now reached a stage that Marx only claimed as a possibility, a knowledge-based economy depending on the brains of human beings and the social intellect (Dyer-Witheford 2005, 73; Bulut 2011, 161). The brain has become an important productive force in informational capitalism (Fuchs 2008, 200). The last decades of capitalist production have been characterised by an intensification and extension of informational commodities being based on knowledge, ideas, communication, relationships, emotional artefacts, cultural content etc. That is to say, labour is not only based on information, but information and communication are now direct forms of labour. Different types of work include agricultural, industrial and informational labour (Fuchs and Sevignani 2013, 257). Part of this information and knowledge is created and shared by academics at higher education institutions. Universities thus play an important role in informational capitalism.
Autonomist Marxism has raised the concept of the 'common'. The germ form (Keimform) of capitalism is the commodity and the germ form of communism is the common (Dyer-Witheford 2007, 81; Hardt and Negri 2009, 273). A commodity is a good produced for exchange and a common is a good produced by collectivities to be shared with all. The common is the dialectical sublation of private property and public goods.
The capitalist logic has a very contradictory relationship to the common, because it needs and opposes it at the same time (Sandoval 2014, 234). Capital rests on the common and cannot survive without it as well as permanently tries to expropriate and commodify the commons. The commons are produced and reproduced by all, but only appropriated by capital in order to achieve profit. Capitalist accumulation and development paradoxically require and even make possible the expansion of the common and simultaneously tend to destroy it (Hardt and Negri 2009, 153). The capitalist logic is based on collective production and productive subjectivities and depends ever more on the common due to an increased importance of information, communication, knowledge, and creativity for capitalist production. The capitalist command again and again privatises economic, political, cultural, natural, and technological commons and strives to transform them into private properties. Hence, current capitalist accumulation expropriates and destroys the commons.
One can argue that knowledge and skills that are created and shared at universities are part of the commons. Academic knowledge creation can be considered as a social process. Academics create knowledge that is based on preceding knowledge of society, share this outcomes with society so that further knowledge can be created in society, and so on. Academic knowledge creation is the result of a common social process and an infinite social cycle. Students are also involved in producing the knowledge commons, since teaching is not a one-way process. The interaction between lecturer und students can be considered as production and reproduction of educational knowledge. Informational capitalism rests on the knowledge commons that are partly created at universities. On the one hand, capital needs the knowledge as outcome of academic research for pushing innovation forward, on the other hand, capital requires a highly skilled workforce that has been trained in higher education institutions.
Because universities are primarily funded by the state and through tuition fees, capital receives the knowledge commons at no costs. Capital appropriates the commons and thereby exploits the results of the societal production process at universities. Capital exploits the commons and society. The implementation of patents and intellectual property rights are attempts to transform scientific knowledge and academic commons into private properties. Although academic workers and students are not under direct command of capital, they are part of the knowledge workforce producing the commons that are consumed by capital. Academic labour is thus indirectly producing surplus value and exploited by capital. Academic workers and students can be considered as part of what Hardt and Negri (2004) call the 'multitude'. The multitude is an expanded class concept going beyond manual wage labour and taking into account that labour is increasingly based on the commons.
Capital's consumption of the education commons is not an automatic, all-encompassing process. It also leaves space for niches of critical, counter-hegemonic teaching and learning that does not serve capital's interests and cannot be subsumed under capitalism. This form of academic labour is unproductive and does not create surplus value. Although critical research and teaching is tolerated to a certain extent (and tends to be higher at environments where the idea of the neoliberal idea is less advanced), it reaches limitations and constraints since students need vocational training and employability skills for the job market. In addition, institutions and departments being in the tradition of critical, non-valuable education are often confronted with financial problems, redundancies or even closures. Taken globally, this form of education tends to be marginalised and (higher) education clearly serves the interests of capital (Harris 1982, 70). Besides the dimension of commodity critique and academic labour, there is also an ideological level of higher education and universities.
The labour process is a human activity where, with the help of the instruments of labour, and alteration of material is effected. Marx understands the labour process as a relationship of human activity with its physical and intellectual capabilities and the means of production with its instruments and subjects of labour. The productive forces are a system of living labour forces and facts and factors of the process of production that cause and influence labour (Leisewitz 1990, 939). There is a relationship between labouring human actors (subject) and means of production (object) that changes historically and is based on a concrete formation of society such as capitalism. On the one hand, subjective productive forces are the unity of physical and spiritual labour forces of an individual (Marx 1997); that is, physical ability, qualification, knowledge, abilities, experiences, etc. On the other hand, objective productive forces are factors of the process of labour and production that are not related to an individual; that is, objects of labour such as resources and raw materials and instruments of labour including technology.
Similarly, academic work is an activity where academics transform and organise with the help of instruments an object in order to produce an academic outcome. The productive forces are a system of academic workers and facts and factors of the process of production that cause and influence academic labour. The relationship between academics (subject) and means of production (object) forms the productive forces of universities. On the one hand, subjective productive forces are the unity of physical and intellectual abilities of academics. On the other hand, objective productive forces are factors of the process of academic labour; that is, objects of academic labour such as knowledge, skills and practices and instruments of academic labour including libraries, computers, laboratories and equipment. Academics make use of libraries, computers, laboratories and equipment in order to produce knowledge, skills and practices and pass it on to society and students. These are 'the general productive forces of the social brain' (Marx 1997). The process is extinguished in the product and includes research outcomes such as publications and technical innovations and teaching degrees hold by bachelor, master and PhD graduates.
Fuchs and Sevignani (2013, 239-249) remind us of the importance of making a semantic differentiation between work and labour in the English language. Work is a creative and productive activity that produces use values in order to satisfy human needs. Work is a general and anthropological concept common to all societies. Labour in contrast is a concrete form of work that produces value. Labour is a historical form of the organisation of work in class societies. It is a specific historical characteristic of work embedded into class relations. Work is essential and takes place in all societies, labour only takes place in capitalism. Because universities are part of capitalism and academics are embedded into class relations, it thus makes sense to speak about academic labour, instead of academic work (Winn 2015, 1). Academic labour is a specific historical form of academic work.
According to Giddens (1981, 64) and Bourdieu (1977, 4), social phenomena are characterised by a mutual relationship of social structures and social actors. Social structures can be understood as institutionalised relationships that enable and constrain the individual. Social actors can be understood as human individuals that act within and might react on social structures. Social phenomena consist of social structures enabling and constraining social actors that react upon social structures. Academic work is also characterised by a mutual relationship of social structures and social actors; or speaking more specifically, of form and content. The social structure and form of academic work can be understood as the political, economic and cultural context of universities. This includes political power relations, the economic structure and cultural hegemony of academic labour and to see universities as institutions within capitalism. These structures do have an enabling and constraining effect on academics. Structures enable academics in the sense that they make possible work in the first place. For example, universities provide employment contracts and material resources and thereby making possible academic work conducted by individuals. But contracts and resources are limited in many ways and thus also constrain individuals and academic work. The social actors can be understood as human individuals conducting academic work resulting in academic content. This includes the academic as subject creating a certain outcome of academic knowledge, skills and practices, the analysis and assurance of the quality and values of this outcome and the pedagogical impact. Social actors might react on social structures within universities. Social structures are the historical outcome of struggles and thus changeable to a certain extent. For example, salary bargaining, reduced workloads, additional resources, new staff etc. are possible reactions of academics to the social structure within universities. These new social structures again have an effect on individuals. Academic work is thus a permanent process of social structures enabling and constraining individuals that react upon social structures.
Yet, Winn (2015, 1-2) argues that there is a tendency within the existing literature to focus on the content of academic practice, values of as well as teaching and assessment in higher education, concerns with identity and what it subjectively means to be an academic. Such a focus is one-sided, undialectical, leaves out the political economy of higher education and critical engagement of capitalism. Bringing back the relationship between the political-economic context and the academic as worker within academic labour studies is the focus of this paper and my on-going research. The distinction between form and content of academic labour is related to the distinction between relations and forces of production. Both the content of academic work and productive forces consider the particular production process and the form of academic work and relations of production take into account the social context of this process. Talking about the content and omitting the form of academic work is similarly as problematic as talking about specific forms of the organisation of the productive forces, cumulated in terms such as 'information society' or 'network society', and omitting questions of the relations of production with regard to ownership, power and division of labour.
As outlined in the previous section, although the university as a place of academic knowledge creation has a long tradition, its development from an intellectual circle of elites to a broader institution of higher education can be considered as medium and outcome of informational capitalism. The realm of academia is a specific subsystem of the information and knowledge sector. Academic work is a specific form of information work that has to do with the production and distribution (reproduction) of academic knowledge, skills and practices. Because culture entails information work creating content and communication, academics can be considered as cultural workers (Gill 2014). In sum, academic work is part of informational work that is part of cultural work. 'Artistic and academic traditions extol sacrificial concepts of mental or cultural labour that are increasingly vital to newly important sectors of the knowledge industries' (Ross 2000, 2). The strong relationship between universities and neoliberalism indicates how the spheres of culture and economy are interrelated.
Academic work is linked to other forms of work such as clerical, technical and manual work. Many different forms of work are directly and indirectly involved in the creation and sharing of information and knowledge at universities beyond the academic activities of scholars. Think for example of the secretary who organises the administration behind teaching, the librarian who arranges books and journals, the IT technologist who maintains the websites and servers at universities, the manual worker who services the equipment in classrooms, the cleaner and janitor who keep the university building running, etc. Academic activities would hardly be possible without all these different forms of labour at universities. This just indicates that work tends to be a social process where many individuals are involved and what Marx termed 'Gesamtarbeiter' (collective worker). Marx argues that work tends to be a combination of workers, a combined labour force, resulting in a combined product. 'In order to work productively, it is no longer necessary for the individual himself to put his hand to the object; it is sufficient for him to be an organ of the collective labourer, and to perform any one of its subordinate functions' (Marx 1976, 643-644). If we take a look at the higher education landscape in Scotland, one can see how many other forms of work are involved beyond academic work at universities. 19,250 academics, 10,515 academic atypical staff and 23,650 non-academic staff worked at Scottish universities in 2014/2015 (Higher Education Statistics Agency 2016). That means 44.3 per cent are non-academic workers such as administrators, technologists, manual workers etc. at universities. If we talk about labour at universities, one should not oversee this form of work and workforce that comprises almost half of the workers in absolute numbers at least in the Scottish context. To be precise, one could make the distinction between academic work of research and teaching and academic work of administration and technological assistance at universities. However, these tasks are overlapping to a certain extent; for example, academic workers also have to conduct administrative tasks such as keeping registers of their student cohort. Similar to a broad definition of cultural labour (Fuchs and Sandoval 2014, 488), taking into account all different forms of work that are directly and indirectly involved in the creation and sharing of academic knowledge (1) avoids an idealistic understanding of academic work that ignores its materiality, (2) considers the connectedness of technology and content and (3) can inform political solidarities between different groups within universities.
2.2. Conditions of Academic Labour
The neoliberal restructuring of universities led to transformations such as reducing public expenditure, squeezing costs, allocating resources based on competition and quasi-market disciplines. These structural transformations have an effect on the working conditions, practices and relations of subjects within universities. This is also reflected in a growing academic literature reporting about the changes in the working conditions, especially at places where the neoliberal restructuring can be considered as relatively advanced and has been going on for some decades such as the UK, Netherlands, US and Australia (Lorenz 2012, 600).
Sandoval (2013, 323-325) provides a systematic model of working conditions based on Marx' circuit of capital accumulation that can be applied to different sectors. The model identifies dimensions that shape working conditions in the capital accumulation process. In addition, the model includes the impact of the state's labour legislation on working conditions.
- Means of production: objects (resources) and instruments (technology) of labour
- Labour power: workforce characteristics, mental and physical health, work experiences
- Relations of production: labour contract, wages and benefits, labour struggles
- Process of production: labour space, labour time, work activity, control mechanism
- Commodity: labour product
- The state: labour legislation
The model helps to systematically analyse the labour process and can also be applied to academic labour. The overall aim of this section is to introduce an overview of working conditions at universities.
- Means
of production: objects (resources) and instruments (technology) of
labour
Resources: Resources
in the academic labour process consist of knowledge, skills
and practices of the human brain and hands.
Technology:
Technologies that are used in the academic labour process include for
example libraries, computers, laboratories and equipment.
- Labour
power: workforce characteristics, mental and physical health, work
experiences; we can also add unemployment
Workforce characteristics: Important characteristics of the workforce are class, gender, ethnicity, age and disability. Altogether, there are 273,895 academics (part- and full-time academic staff and academic atypical staff) in UK higher education. 37.0 per cent of full-time academic staff have contract salaries between £43,325 and £58,172. Higher proportions of male full-time academic staff (25.3 per cent) have contract salaries of £58,172 or over than female full-time academic staff (13.9 per cent). The proportion of academic females is 45.0 per cent. For full-time academic staff the proportion of females is 40.0 per cent and for part-time 55.1 per cent. 47.2 per cent of the academic atypical staff population are women. 13.9 per cent of academic staff and 17.2 per cent of academic atypical staff are ethnic minorities with a background such as Black, Asian, Chinese and mixed. 4.1 per cent of academic staff and 2.4 per cent of academic atypical staff declared a disability. The average age of full-time academic staff is 43 years and of part-time academic staff 46 years. The average age of academic atypical staff is 40 years. Among other characteristics, young women with a minority background are most likely to work precariously in UK higher education (Bryson and Barnes 2000, 209). In addition, the higher the hierarchy, the fewer women one can find in higher education. For example, 56.2 per cent of students in the UK are female, but only 23.1 per cent of the professors are women (all data for the academic year 2014/2015: Higher Education Statistics Agency 2016).
Mental and physical health: Different empirical studies have reported about mental and physical health issues at higher education institutions. In a survey of the University and College Union (2014, 2), 60 per cent of the respondents showed evidence of some level of psychological distress. According to Watts and Robertson (2011), the burnout level amongst teaching staff at universities is comparable with 'at risk' groups such as healthcare professionals. The psychological distress of academics exceeds many other professional groups and is caused by factors such as high level of conflict between work and private life (Kinman and Wray 2013, 6). Academic and academic-related work tends to 'spill over into the home domain both physically (e.g. working at home during evenings and weekends), and psychologically (e.g. preoccupation with work problems, difficulties in sleeping, and irritability with family and friends)' (Ibid., 7).
Work experiences: The question of how academics experience their working conditions is an empirical one. Several authors have already conducted empirical work in this context. For example, Prichard and Willmott (1997, 313-314) ran 36 interviews with senior post holders such as chancellors, heads and deans at 4 pre- and post-1992 universities in the UK about their experiences, consequences and changes of work. Archer (2008, 269) conducted eight semi-structured interviews with early-career academics at different universities in England about their identities and experiences in higher education. Deem et al. (2007, 33) realised a large-scale project about managerialism, management practices and organisational forms at universities in the UK between 1998 and 2000. The authors carried out in phase one 12 focus group discussions with academics, managers and administrators, in phase two 137 qualitative interviews with manager-academics and 29 senior administrators in 16 pre- and post-1992 universities and in phase three interviews with employees from manual workers to staff at four universities. I conducted 10 semi-structured, face-to-face, qualitative interviews with academics. Focus was given to people who are employed 'atypically' such as on a fixed-term contract, casual contract, hourly paid basis, zero-hour contract, etc. at higher education institutions in Scotland. The scripts were analysed in order to find answers to my questions about how academics perceive the existing working conditions that are shaped by political and economic contexts (Allmer 2018).
Unemployment: For Marx (1976, 790), the working class consists of an active army of workers and a reserve army of unemployed. The unemployed are not a social group outside, but rather part of class relations fulfilling certain functions in and therefore necessary for capitalist societies as they 'become a condition for the existence of the capitalist mode of production' (Ibid., 784). Firstly, the unemployed play an important role as reserve being available if needed. Secondly, the unemployed are also important ideologically in order to keep pressure on those within the production process (Ibid., 785). The employed and unemployed condition, but simultaneously exclude each other in capitalism. The vast expansion of higher education in the last decades has also led to a massive increase in graduates and doctoral students and thereby automatically contributed to the expansion of the academic reserve army; or at least, to an expansion of a social group willing to accept precarious working conditions for a certain period in their lives, before reaching a more secure post. Universities are nowadays able to choose from a pool of mainly early-career academics if needed in times of high demand (Shumar 1995, 94). The unemployed and precariously employed academics compete with each other and try to perform well for the sake and prospect of employment and a more secure post. An ideological pressure and disciplinary mechanism on employed academics is in place as they could be easily downgraded or even replaced by some from the surplus labour pool. 'One of the consequences of the vast expansion of post-secondary education in North America and Europe has been the gradual establishment of a huge pool of surplus researchers, instructors and laboratory assistants, drawn from the ranks of graduate students, whose prospects for permanent academic employment are scandalously low' (Dyer-Witheford 2011, 281).
- Relations of production: labour contract, wages and benefits, labour struggles
Labour contract: One important aspect of an academic employment contract is its permanent/open-ended or temporary character. Many different forms of temporalities exist, including fixed-term, hourly paid and zero hour contracts. A tendency of casualisation and temporality of employment characterises higher education in the UK. According to the Higher Education Statistics Agency (2016), 128,300 permanent/open-ended and 70,035 fixed-term academic staff worked at universities in the UK in the academic year 2014/2015. On top of that, there were 75,560 academic atypical staff in the same year. Summing up those on a fixed-term contract and the academic atypical staff means that the majority (53.2 per cent) work on a temporary basis in UK higher education. Casualisation allows the university to test the performance of the academic, strengthens Darwinian selection, reduces labour costs and gives the opportunity to respond quickly to changes on the education market in order to deal with low and high peaks of demand (Bryson and Barnes 2000, 193). The amount of staff needed also depends on how successful a university is in terms of marketing and attracting students for the upcoming academic year. Universities compete with each other on a market of potential new students. Casualisation of academic staff can thus be considered as an outcome of applying quasi-market, neoliberal rules at higher education institutions. 'The university could never be sure about enrolments size or profitability; it had to remain forever poised to take action, to stimulate enrolment, to cut costs, to keep growing. The permanent flexibility this required meant that the staff had to be proletarianized and stratified into temporary part-time workers, permanent teachers and permanent researchers' (Shumar 1995, 94). Pratt (1997) highlights that employing part-time and fixed-term staff at universities has become a management strategy. Those working at a pre-92 university, are on research only contracts, work part-time, have up to five years work experience, are female and under the age of 40 as well as non-white and non-UK are most likely to be on temporary contracts (Bryson and Barnes 2000, 209). Temporary contracts tend to have an impact on the employee's economic security and control, exclusion from the department, relationships with other colleagues, and a lack of opportunity for career development and promotion (Ibid., 217). Gulli (2009, 5) highlights that the expansion of temporary staff is typical for the neoliberal discourse as it brings flexibility to the university at the cost of individual insecurity that can lead to anxiety, disruption, stigmatisation and loss of dignity. A contradiction between inclusion and exclusion characterises the employment of temporary staff as it is much needed and included in economic terms, but tends to be invisible and exposed and therefore excluded in social and political terms. Tirelli (1999) therefore stresses that casual contracts trigger labour segmentations within the academic workforce leading to increased hierarchies and potentials of conflict. Neoliberal universities tend to decrease the number of established and respected permanent staff and increase the number of relatively powerless temporary staff. From a trade union point of view, casualisation brings also political changes that advantages the management and weakens the academic workforce. 'Faced with a restive mass of immaterial labour, university administrator's best strategy - backed by centuries of academic hierarchy - is to ensure that regular and contingent faculty remains divided' (Dyer-Witheford 2005, 78).
Van Dyk and Reitz (2016) argue that universities are becoming what Boltanski and Chiapello call the 'projective city'. The projective city signifies the idea of the new spirit of capitalism that is based on projects sparking temporary compression of networks, competition of project teams on the market and new work ethics and forms of employees' motivation. 'This refers to a firm whose structure comprises a multiplicity of projects associating a variety of people, some of whom participate in several projects. Since the very nature of this type of project is to have a beginning and an end, projects succeed and take over from one another, reconstructing work groups or teams in accordance with priorities or needs' (Boltanski and Chiapello 2007, 105). Statistics confirm this trend for the Scottish higher education landscape: 72.9 per cent of the total annual research income for Scottish universities is gained from research grants and contracts such as research councils, societies, charities, corporations, EU sources (for the time being) etc. In comparison, only 27.1 per cent go directly to the universities in form of recurrent research income as result of the Research Excellence Framework (all data for the academic year 2014/2015: Higher Education Statistics Agency 2016). Most of these funds are project-based and competitive. Academics employed in such projects mainly work on a temporary basis.
Wages and benefits: The question of wages and benefits is a relational one. Considered historically, academics have been a relatively privileged group of employees (Callinicos 2006, 24). If one compares the salary and social advantages like annual leave entitlement or pension benefits to other groups such as social and health workers, one has to admit that academics still enjoy benefits that are not or not any more available in other sectors. But there is a contingent struggle in terms of academic salaries and benefits. Callinicos (2006, 25) stresses that academics have seen their pay stagnated in real terms and declined relatively in the last century. The University and College Union (2016c) highlights a 14.5% loss in real terms of salaries in higher education measured against inflation since 2009. Pay scales are also highly stratified in the higher education sector. For example, the vice chancellor (or equivalent) at the University of Strathclyde, Glasgow, receives an annual salary of £343,000. In contrast, a FTE (full-time equivalent) annual salary of an hourly paid academic at the same university is £17,995 (with an assumed hourly rate of £23) (all data for the academic year 2014/2015: University and College Union 2016b). This means the vice chancellor earns 19 times more than an hourly paid academic at the University of Strathclyde. Similar calculations can be worked out for other universities.
Labour struggles: As already mentioned, academics have traditionally been a relatively privileged group of employees and universities were historically considered as communities with shared values and interests in the UK. This was also reflected in absorbed labour struggles and a weak union of higher education. Consequently, the Association of University Teachers (AUT) did not see itself as a trade union, but rather as a professional association (Callinicos 2006, 24). In contrast, academic staff in the post-1992 universities and college teachers enjoyed less privileged conditions in the past. Their union, the National Association of Teachers in Further and Higher Education (NATFHE), has 'developed a much more militant tradition of trade unionism, and has tended to be led from the left' (Ibid., 25). Supported by the fact that this union also represented college teachers, who were already confronted with a rather brutal neoliberal reorganisation. The two organisations merged in 2006 to the University and College Union (UCU). Callinicos (2006, 36) notices that the material conditions of neoliberal restructuring in higher education in the last decades have resulted in a more active trade unionism among academics in general. The University and College Union has today more than 100,00 members and its policies include the fight against the privatisation of education, casualisation, workload and stress as well as organising the collective pay bargaining for academic staff. According to Harvie (2006, 21), the opposition of academic unionism is nowadays more or less opposition to neoliberalism.
- Process of production: labour space, labour time, work activity, control mechanism
Labour space and time: In analogy to the idea of the factory without walls from Autonomist Marxism, Gill (2010) argues that the neoliberal university can be considered as academia without walls. Autonomist Marxism claims that capital tends to subsume the whole society into the production process and the logic of the factory is extended to society (Wright 2002, 37-38). Society functions as a moment of production, where the boarder between working and spare time becomes more and more blurred (Gorz 2010, 22) both spatially and temporally. The social factory is therefore a 'factory without walls' (Dyer-Witheford 1999, 80). Likewise, neoliberal universities have intensified work in terms of time and extended in terms of space with the help of digital technologies. Academics tend to have fluid boundaries between their working space and other spaces of human life and their labour and free time (Ross 2000, 23). Always-on cultures have transformed the university to a fast academia. 'Ever speeded-up mobile technologies intermesh seamlessly with the psychic habitus and dispositions of the neoliberal academic subject: checking, monitoring, downloading whether from BL (British Library), beach or bed, trying desperately to keep up and "stay on top"' (Gill 2010, 237). This indicates how a technological change of the productive forces can have an effect on the working conditions within the production process.
This theoretical assumption can be underpinned with empirical data. The University and College Union has conducted several online surveys about workload and work-related stress in the UK (Court and Kinman 2009; Kinman and Wray 2013; University and College Union 2014; 2016a). In 2014 (n=6,439), 79 per cent of the participants agreed or strongly agreed that they find their job stressful. 53 per cent indicated that their general or average level of stress was high or very high. Almost half (48 per cent) responded that they experience often or always unacceptable levels of stress (University and College Union 2014, 1-2). According to the 2016 survey (n=12,113), academic staff works an average of more than 50 hours FTE per week. Especially amongst early career academics exists a culture of long working hours (University and College Union 2016a, 18). Factors contributing to stress in higher education include among others the lack of time to undertake research, excessive workloads, problems in obtaining funding, lack of promotion opportunities and job insecurity (Court and Kinman 2009, 61). Academics tend to regularly work evenings and weekends in order to cope with the high demands of their job (Gill 2010, 235) and not taking their full entitlement of annual leave (Crang 2007, 510).
Work activity: A tendency of narrow specialisation, routine tasks, division and standardisation of work characterises academia. Teaching and research are becoming increasingly separated (Liesner 2006, 484). Especially casualised staff is confronted with a lack of autonomy in teaching, break down of teaching into isolable units, decreasing authority of the individual educator and predefined and predesigned modules and programmes that potentially lead to frustration and dissatisfaction. In analogy to the assembly line worker, Hanley (2002, 30) describes this process as 'Taylorization of academic labor'. Harvie argues that school and university teachers become alienated from their work activity, an activity that does not belong to them. 'The very separation of knowledge into more-or-less well-defined and discrete "disciplines" or "subject's" constraints the majority of teachers within "their" subject's boundaries' (Harvie 2006, 10-11). Similar, research is becoming gradually homogenised due to 'hot topics' and increasing difficulties in obtaining funding. Lorenz (2012, 613) states that intrinsic satisfaction has been replaced by externally driven rewards.
Control mechanism: Although procedures of surveillance, monitoring and audit cultures are no new control mechanisms within universities (for example: the Research Assessment Exercise has been in place since the 1980s), nor is the university by far the only place of surveillance (see: Allmer 2012), they have been taking hold significantly at higher education institutions in the UK for some years now (Burrows 2012, 357). Metrics operate at different stages such as the institutional, national and international level, but all of them confront the individual academic (Burrows 2012, 359). New information and communication technologies have helped to intensify and extend these procedures, which indicates the link to the means of production. An elaborate set of monitoring procedures and metrics exists at universities, including grant income, citation scores, workload models, transparent costing data, research 'excellence', student evaluation, employability scores, impact factors and commercial university league tables (De Angelis and Harvie 2009, 11-14). Burrows (2012, 359) identifies that British academics are now subject to more than 100 different scales and indices. Academics are measured individually against other colleagues as well as grouped and measured against other groups in order to assess and rank academic values. Gill (2014, 22-24) argues that surveillance culture and audit regimes lead to a new psyche and structures of feeling at universities that includes individual pressure, anxiety and threats. The proliferation of league tables triggered a culture of naming and shaming that results into self-surveillance. 'Being hard-working, self-motivating and enterprising subjects is what constitutes academics as so perfectly emblematic of this neoliberal moment, but is also part of a psychic landscape in which not being successful [...] is misrecognised [...] in terms of individual (moral) failure' (Gill 2010, 240).
'New managerialism' is another control mechanism that has been implemented at higher education institutions in the last decades. New managerialism can be understood as the adoption of organisational forms, technologies, managerial control practices and ideologies from the private business to the public sector such as universities (Deem, Hillyard and Reed 2007, 24-28). As response to the post-Fordist conditions, UK universities are becoming increasingly corporately managed. Academic professions are thereby broken up into controllable processes (Lorenz 2012, 610). The private sector style of management includes the realisation of a hierarchical organisation structure, division and standardisation of work, narrow specialisation and routine tasks in order to increase accountability and measurement by management. Prichard and Willmott (1997) highlight that universities implemented many elements of 'soft managerialism' urging academics to meet performance targets and thereby encouraging self-discipline without the need of 'hard management'. As a result of the pressure to meet performance objectives, individual resources for actively participating in the decision-making process on the institutional and school level are becoming scarce. 'Yet, in effect, increased managerialism implies that the input of staff into decision-making is degraded from collegial participation to, at best, a consultative role in which staff willingly accept and support their heads of department who then managerialize the process through which resources are won and allocated' (Willmott 1995, 996). Tancred-Sheriff (1985, 384) compares the decision-making process at universities with a 'kiddie steering wheel in daddy's car' with heaps of relatively powerless committees and panels, despite formal decision-making powers. Prichard and Willmott (1997) conducted 36 interviews with senior post holders such as vice-chancellor, dean, head of school and head of department at four UK universities about their understanding of managerialism. The authors report that their interviewees 'talked of the implementation of strategic initiatives, of managing staff, of taking responsibility and even of being a small-businessman' (Prichard and Willmott 1997, 313). Miller (1991, 111) argues that vice-chancellors tend to act like chief executives.
- Commodity: labour product
Labour product: The work of academics results into research outputs such as publications and technical innovations and teaching degrees hold by bachelor, master and PhD graduates. Many research outputs are published by for-profit academic publishing companies such as RELX (former Reed Elsevier), Springer, Taylor & Francis and Wiley-Blackwell and appear in corporate databases such as the Thomson Reuters' Science and Social Science Citation Indexes. These industries are highly monopolised, commodify and thereby restrict access to academic knowledge, have the power to decide who is 'in' and 'out', and privatise knowledge being produced in publicly funded research institutions (Hall 2008). Harvie (2006, 12) mentions that the work of school and university teachers' results into graduates who are supposed to be bearers of a range of knowledge, skills and attributes. But those skills tend to correspond to valuable labour power skills, increasingly determined by the needs of capital. Teachers produce labour power for capital and are thus alienated from the product of their labour.
- The state: labour legislation
Labour legislation: McGettigan (2013) argues that the broader vision of higher education in the UK is that the state rolls back gradually through processes of privatisation and the remaining public areas are characterised by quasi-market regulations. Different processes, policy considerations and initiatives have been brought forward in this context (Ibid., 9):
1. 'Marketisation or external privatisation, whereby new operations with different corporate forms are allowed to enter the state system to increase competition. This might be seen as dissolving the distinction between separate public and private sectors.'
2. 'Commodification - the presentation of higher education as solely a private benefit to the individual consumer; even as a financial asset where the return on investment is seen in higher earnings upon graduation.'
3. 'Independence from regulation - private providers accessing the student loan book are not bound by numbers controls and do not have to comply with reporting or monitoring requirements nor widen participation initiatives.'
4. 'Internal privatisation - the changes to revenue streams within institutions so that for example, direct public funding is replaced by private tuition fee income.'
5. 'The outsourcing of jobs and activities to the private sector and management consultants, which has become widespread in England.'
6. 'Changes to the corporate form and governance structures of universities.'
7. 'The entry of private capital and investment into the sector through buyout and joint ventures with established institutions.'
Table 1 summarises the conditions of academic labour with the key elements of each of the dimensions in the capital accumulation process and the impact of the state.
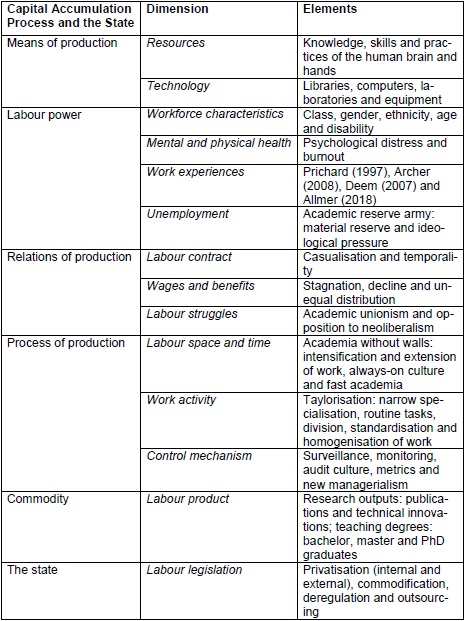
Table 1: Conditions of Academic Labour
All of these dimensions shape the working conditions at higher education institutions to a certain extent. Based on these insights, I now move on to the impact of new information and communication technologies on universities and academic labour.
3. Digital Academic Labour
The academic work process is today strongly linked to the use of new information and communication technologies such as email communication, online education and digital registers for research, teaching and administration purposes. The use of technologies is not a new phenomenon at universities and one can argue that academics have always used some sort of technology as means for their work. For example, the chalk and blackboard served for many decades as an important tool in order to share knowledge in the classroom and was later accompanied by the overhead projector. The communication between university teachers and distance learning students used to take place via traditional letters sent by snail mail (Noble 2001, chapter 1) and is today fully replaced by digital communication. One can argue that educational technologies have been developed in analogy with the progress of the productive forces and reflects the historical development from agricultural to industrial to informational eras in capitalist societies. Although the application of technologies at universities is not new, the use of digital technologies is a relatively new phenomenon and has generated a rapid quantitative expansion that simultaneously raises questions of a qualitative shift. A gradual expansion of educational technologies (quantity) led to a new digital realm at universities (quality). The application of education technologies can thus be considered as a new and at the same time old development. A dialectics of continuity and discontinuity characterises the development of educational technologies.
Digital media are used for different research and teaching purposes. Here is an indicative list of different possibilities in using digital media for research:
- Online libraries
- Digital books and journals
- Online database
- Online research and digital methods
- Digital communication
- Virtual networks and conferences
Here is an indicative list of possibilities how new information and communication technologies are used for teaching and learning:
- Virtual learning environments such as Moodle and Blackboard
- Digital classroom
- Online lecture
- Wikis, Blogs and online discussion boards and forums
- Online video chats and voice calls
- Online tutorial, supervision and marking
- Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs)
Digital academic labour is a specific form of academic labour that is mediated through digital media. Digital and non-digital media and resources often co-exist in the work experience of academics. One might think of someone, who uses Blackboard for teaching in order to upload documents for students and supervises students via email, but teaches in a physical classroom. Another example might be that researchers browse the library catalogue online, but still prefer to read the hard copy of a book. Digital technologies and resources have neither displaced non-digital ones fully, nor are non-digital technologies and resources completely independent of digital ones. It is as hard to imagine an academic who is able to manage his work without the use of digital media, as it is an academic without the use of non-digital media. Different people have different degrees in blending digital and non-digital media at their work.
While the pedagogical impact of digital media is not the focus of this paper, I would like to draw your attention to the economic aspect, especially in the context of teaching. According to McGettigan (2013, 115), the total annual income of UK universities is around £30 billion and more than 50 per cent come through teaching via tuition fees and public grants. Overseas tuition fees, i.e. fees from students from outside the EU such as China, play a crucial role in income for universities in the UK (McGettigan 2013, 117). Higher education institutions today compete on a global market for international students. Recruiting oversea students is particularly appealing in the UK, because institutions are not bound by the same restrictions as they are with Home and EU students (for the time being) - there is no cap in terms of fees and in terms of numbers. Generally speaking, there are at least three different possibilities to reach international students.
1. Foreign students come to the UK for studying at one of the universities
2. British universities install a branch campus abroad
3. Both remain in their home country and teaching is facilitated via digital media
The first option seems to be the most obvious one. If we take a look at Scotland, there are almost 30,000 non-EU students. Considered the full-time students separately (overseas students are not eligible to study part-time), 15.1 per cent of the student population in Scotland comes from non-EU countries. At the University of Edinburgh, there are more full-time postgraduate students coming from outside the EU (3,100) than from the UK (2,435) (all data for the academic year 2014/2015: Higher Education Statistics Agency 2016). There are political restrictions in recruiting non-EU students. Partly because the government has declared a target to reduce migration, which should also apply to students (McGettigan 2013, 121) and brings some uncertainty in terms of economic planning for universities. Partly because the recruitment of overseas students and the accompanied sponsorship of visas brings up immigration rules and an onerous and cost-intensive administrative system for higher education institutions (Ibid.). This includes the proof of language skills and record keeping of attendance and study progress. 'Alternatively, if the students have difficulties coming into the country, then let's take the universities to them' (Ibid.).
The second option is to establish satellite campuses abroad for local students being appealed to receive a degree from a (prestigious) British university. While the official claim is to strengthen international research relationships, it can be considered as a further strategy to access the population of countries such as India, China and Indonesia (Ross 2009, 202). For example, the University of Nottingham has opened up campuses in Malaysia in 2000 and in Ningbo (China) in 2004, now with some thousands students. While there are today more than 200 oversea branch campuses mainly (co-)operated by US, UK and Australian universities, the success is rather limited and the business strategy can be considered as highly risky (McGettigan 2013, 122-123).
The third option is to offer courses and programmes being delivered by means of digital media (online distance learning). From a technical point of view, online teaching requires teachers and students with some hardware (computer and headset), software (as listed above) and an Internet access, the university mediates this relationship. Online distance learning is technically independent of space and time for both teachers and students as they can theoretically work from anywhere. Those programmes have been primarily brought forward by major higher education institutions such as the Open University and the University of Edinburgh in the UK and Stanford University, Harvard University and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in the US. Because neither the student has to come to the foreign country, avoids being confronted with immigration regulations and saves money for travelling and relocation, nor has the university to invest in new campuses abroad, digital teaching can be considered as a very promising business strategy in recruiting more overseas students, although it also attracts UK and EU students.
The three different possibilities are not a linear historical development, where one attempt replaced the other, but rather a complex and contradictory field of changing strategies and economic ups and downs in the higher education market. These practices co-exist simultaneously, but digital education seems to be the most promising at the moment. The Higher Education Funding Council for England (HEFCE) (2009, 7) is quite clear on this matter: 'Effective use of technology [...] can also help institutions in [...] attracting overseas students [...] Distance learning [...] will [...] assist with the recruitment and retention of (international) learners'.
For Marx, the mode of production is based on productive forces (means of production and labour power) and relations of production (property relations). The productive forces are a system of living labour forces and facts and factors of the process of production that cause and influence labour (Leisewitz 1990, 939). The relations of production constitute social relations between human beings and specify who produces and who owns property (Krysmanski 1990). If we take a look at the mode of production at universities, one can see that the productive forces and relations are changing in the realm of digital education.
Productive forces: Although digital education causes new costs (for example for licence fees of digital software), universities are able to reduce the means of production such as buildings, equipment and facilities as they are outsourced to individuals and the private sphere. While students visit lecture halls, seminar rooms, laboratories, libraries etc. operated by the university for brick and mortar campus teaching, students visit a virtual space, but are physically at a private or other space of human life with an electronic device in the age of digital education (van Mourik Broekman et al. 2015, 22-23). In addition, the university has to invest in technologists who establish and maintain digital learning environments, but digital education potentially reduces labour costs in the long term due to reproducibility. One can imagine an online module conceptualised to watch recorded lectures by research-intensive professors and receive tutorials and supervision by cheap labour power such as teaching fellows and hourly-paid lecturers (Noble 1998). Different universities have different digital practices, but online distance learning can reduce labour power as lectures can be easily recorded and replayed, accompanied with some individuality. 'The marriage of corporate culture, higher education, and the new high-speed technologies also offers universities big opportunities to cut back on maintenance expenses, eliminate entire buildings such as libraries and classrooms, and trim labor costs' (Giroux 2002, 447). Due to the reduction of the productive forces, digital education can both provide a cost-efficient alternative and bring flexibility for universities in order to be able to respond quickly to changes in the higher education market in terms of demand (Massy and Zemsky 1995). An online module can be theoretically provided very quickly due to reduced material necessities and thus makes it likely to react appropriately to economic ups and downs on the student market.
Relations of production: Digital education poses new questions of intellectual property rights. Because ownership tends to follow authorship in copyright law, teaching staff traditionally owned their course material (Noble 2001, 38). This has been a long-established tradition and right at universities. If an academic left university, s/he had the right to take teaching material with him/her and was able use it for other purposes, because it belonged to the creator of educational content. As argued above, digital education can only reduce labour power and costs, if content can be recorded and reused (reproducibility). One could imagine a situation where a university aims to use recorded lectures and stored communication for an online module being originally developed by teaching staff, not working for this institution anymore. In case the university is not licensed to use this content, it could end up in either legal or economic problems. Higher education institutions thus have a strong interest in getting the intellectual property rights and licences of the developed teaching material. Universities must control the copyright. Different countries do have different practices, but it seems as the US higher education market is the most advanced in this context at the moment (Noble 2001, chapter 3). 'Ivy League schools have, in fact, developed some of the most aggressive and sophisticated examples of commercial online education' (Werry 2002, 35). Noble (2001, 38) argues that research has already been commodified, but with digital education, course material follows a similar pattern. For research tasks, employees are contractually required to assign the patent rights to the university as routine condition of employment. Similarly, employees might be forced to assign the copyright and licence of course material stored on PCs, websites and courseware as routine condition of employment in the realm of online teaching. This transforms the nature of teaching and the relationship between higher education institutions and their employees. 'Like the commercialization of research, the commercialization of instruction entails a fundamental change in the relationship between the universities and their faculty employees. Here faculty who develop and teach face-to-face courses as their primary responsibility as educators are transformed into mere producers of marketable instructional commodities that they may or may not themselves "deliver"' (Ibid.).
Digital education and technologies have an impact on the working conditions of academics. If we reconsider the different stages of the capital accumulation process as outlined in the previous section, one can see the risk that conditions of labour are being intensified and extended in the realm of digital media; to name but a few, the blurring of working space and other spaces of human life, the blurring of labour and free time, fast academia, always on cultures, deskilling, casualisation, electronic monitoring, digital surveillance, social media use for self-promotion, and new forms of intellectual property rights (Noble 1998; Gregg 2013; Lupton 2014, 79-83; Poritz and Rees 2017, 68-82).
One could argue that digital education and technologies widen access for people from poorer backgrounds, women, ethnic minorities and disabled and thereby provide inclusion, equality of opportunities and social justice. For example, HEFCE (2009, 7-8) promotes that technologies enhance learning and teaching that open access and opportunity and bring equality of access, inclusion, flexible lifelong learning and international mobility. The argument that new technologies in education automatically bring enhancement can be considered as a techno-optimistic and techno-deterministic view that tends to ignore the social sphere and sees technology as being independent of its social context (Bayne 2015, 5). For example, it is difficult to imagine how digital education should widen access for people from poorer backgrounds, if such programmes tend to be rather expensive with similar fees as their offline companions. Digital education can bring advantages for disabled people, being able to study at their own pace, but might involve the risk of new forms of social exclusion. Noble (1998) draws a possible future where digital education will become the second-class education, while traditional on-campus teaching will become the exclusive privilege of the rich and the powerful - the poor get a computer, the rich get a computer and a teacher. 'In the case of distance education, however, the digital divide is turned on its head, with the have-nots being compelled to take their courses online while the haves get to do it in person' (Noble 2001, 90). In similar vein, Giroux (2002, 448-449) argues that 'a class-specific divide begins to appear in which poor and marginalized students will get low-cost, low-skilled knowledge and second rate degrees from online sources, while those students being educated for leadership positions in the elite schools will be versed in personal and socially interactive pedagogies in which high-powered knowledge, critical thinking, and problem-solving will be a priority, coupled with a high-status degree'.
Universities are keen on promoting that their offered online programmes are internationally recognised degrees and of equal value to on-campus programmes (for example: University of Edinburgh 2016), but the risk still exists that employers tend to favour on-campus degrees when it comes to the recruitment process (Linardopoulos 2012; Fogle and Elliott 2013). Given the fact that digital technologies in higher education are still in a relatively early stage, the development of the cohort in terms of social background is difficult to predict and remains an empirical question. But it gets clear that online education fits neatly within the neoliberal agenda. An increasing need of a highly qualified, skilled and trained workforce characterises contemporary capitalism that leads to higher pressure of further education and lifelong learning processes. People tend to live under stressed and tightened circumstances, fulfilling several tasks and commitments such as full-time jobs and family and social relations at the same time (Rosa 2013). Digital education helps to compensate this dichotomy by offering a higher education qualification in a very flexible route as it tends to be independent of time and space. Digital education can thus be considered as a response to neoliberal conditions.
4. Conclusion and Alternatives
Based on a critical social theory approach and moving from the abstract to the contract level, this article has engaged with the history and context of universities, dealt with the forms and concepts of academic labour and provided a systematic analysis of working conditions at higher education institutions. It has furthermore discussed the impact of new information and communication technologies on academic labour.
According to Winn (2015, 4, 10), the academic labour studies literature tends to deal with historical, theoretical and critical questions inadequately. The aim of this article has thus been to contextualise universities historically within capitalism and to analyse academic labour and the deployment of digital media theoretically and critically. The key arguments can be summarised as follows:
- Historical context: The post-war expansion of the university can be considered as medium and outcome of informational capitalism and as a dialectical development of social achievement and advanced commodification.
- Academic labour: Academic workers and students are part of the knowledge workforce producing the commons, indirectly creating surplus value and exploited by capital. Academic labour is a specific historical form of academic work. Academic work is part of informational work that is part of cultural work. A broad definition of university labour, taking into account all different forms of work that are directly and indirectly involved in the creation and sharing of academic knowledge, can inform political solidarities between different groups within universities.
- A theoretical model of working conditions helps to systematically analyse the academic labour process and to provide an overview of working conditions at universities. The following dimensions shape the working conditions at universities: resources, technology, workforce characteristics, mental and physical health, work experiences, labour contract, wages and benefits, labour struggles, labour space and time, work activity, control mechanism, labour product, and labour legislation.
- Digital media: The academic work process is today strongly linked to the usage of new information and communication technologies. A dialectics of continuity and discontinuity characterises the development of educational technologies. Digital academic labour is a specific form of academic labour that is mediated through digital media. The deployment of digital media has an impact on the working conditions of academics, including the blurring of labour and free time, fast academia, and electronic monitoring.
I recently conducted interviews with precariously employed academics in Scotland(see Allmer 2018). One of the results indicates that people value and see the importance of solidarity, participation and democracy. A young researcher tells me that speaking to other precariously employed academics helps to understand patterns of anxieties. She feels it might be better to organise those who are in similar situations and take some agency, instead of feeling alone and powerless:
'There is an awareness that there is loads of us in the same position which is the only comfort about it. I think it does get to the point where you just have to take some agency [...] Maybe we should try and use that, the people who are in a similar position to me, we should actually [...] rather than just feeling like we are alone, we should do something about that, instead of just waiting about.' (Participant 8)
This advances the question about political potentials, challenges and strategies. Wright (2010, 304) distinguishes between three visions of social transformation that correspond broadly to the anarchist, social democratic and revolutionary tradition. The anarchist tradition revolves around social movements, aiming to build alternatives outside of the state; typically the labour movement plays a particular central role in the social democratic tradition, struggling on the terrain of the state; the revolutionary tradition is connected to the Marxist tradition, attacking the state and confronting the bourgeoisie. These strategies should be brought together not only to 'envision real utopias, but contribute to making utopias real' (Wright 2010, 373). In order to avoid pitfalls of co-option and marginalisation on a political level, Wright's vision of the anarchist, social democratic and revolutionary tradition can be connected to the three sections of this article: digital media, academic labour and historical context. Although the deployment of digital media at universities entails the risk that conditions of labour are being intensified and extended, new information and communication technologies can also help to create critical, counter-hegemonic education alternatives outside of the university (anarchist tradition). A broad definition of university labour and a systematic analysis of working conditions point to the need of struggling on the terrain of the university (social democratic tradition). A historical contextualisation of the university within capitalism indicates that the struggle for better universities should aim beyond criticising neoliberal developments and restoring Fordist configurations (revolutionary tradition).
- Digital media - anarchist tradition:Managing the progressive potentials of digital media, we need to establish and engage in critical education alternatives outside the university campus. This could involve open education movements (Winn 2012), open access and copyleft resources (Hall 2008), creative and digital commons, and the Wikiversity (van Mourik Broekman et al. 2015).
- Academic labour - social democratic tradition: We need to reclaim the university as site of struggle for all university workers, including academics, students, clerical, technical and manual workers. This requires solidarity, collectivity, participation, democratisation, resistance, opposition, unionisation (Bailey and Freedman 2011) and can inform political solidarities between different groups within universities (and to find for example commonalities between outsourced cleaners fighting for sick pay, leave entitlement and pension scheme and hourly-paid academic staff at University of London's School of Oriental and African Studies[1]).
- Historical context - revolutionary tradition: We need to connect the struggle at universities with the global struggle against capitalism. As stated in the introduction, modern universities have always been part of and embedded into capitalism in political, economic and cultural terms. 'The struggle for better universities can't be separated from the movement against global capitalism itself' (Callinicos 2006, 7).
These various directions and strategies should be brought together in order to find commonalities of different struggles and contribute to making utopias real.
References
Allmer, Thomas. 2018. Precarious, Always-on and Flexible: A Case Study of Academic Working Conditions. European Journal of Communication: forthcoming.
Allmer, Thomas. 2012. Towards a Critical Theory of Surveillance in Informational Capitalism. Frankfurt am Main: Peter Lang.
Archer, Louise. 2008. The New Neoliberal Subjects? Young/er Academics' Constructions of Professional Identity. Journal of Education Policy 23 (3): 265-285.
Bailey, Michael and Des Freedman. 2011. The Assault on Universities: A Manifesto for Resistance. London: Pluto Press.
Bayne, Siân. 2015. What's the Matter with 'Technology-Enhanced Learning'? Learning, Media and Technology 40 (1): 5-20.
Boltanski, Luc and Ėve Chiapello. 2007. The New Spirit of Capitalism. 2nd ed. London: Verso Books.
Bourdieu, Pierre. 1977. Outline of a Theory of Practice. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Bryson, Colin and Nikki Barnes. 2000. The Casualisation of Employment in Higher Education in the United Kingdom. Academic Work and Life 1: 187-241.
Bulut, Ergin. 2011. Creative Economy: Seeds of Social Collaboration or Capital's Hunt for General Intellect and Imagination? In Cognitive Capitalism, Education and Digital Labor, edited by Michael Peters and Ergin Bulut, 151-168. New York: Peter Lang.
Burrows, Roger. 2012. Living with the H-Index? Metric Assemblages in the Contemporary Academy. Sociological Review 60 (2): 355-372.
Callinicos, Alex. 2006. Universities in a Neoliberal World. London: Bookmarks Publications.
Court, Stephen and Gail Kinman. 2009. Tackling Stress in Higher Education. London: University and College Union. Accessed 11 January 2018. https://www.ucu.org.uk/media/3021/Tackling-stress-in-higher-education-UCU-survey-findings-Dec-08/pdf/ucu_hestress_dec08.pdf
Crang, Mike. 2007. Flexible and Fixed Times Working in the Academy. Environment and Planning A 39 (3): 509-514.
De Angelis, Massimo and David Harvie. 2009. 'Cognitive Capitalism' and the Rat Race: How Capital Measures Immaterial Labour in British Universities. Historical Materialism 17: 3-30.
Deem, Rosemary, Sam Hillyard and Mike Reed. 2007. Knowledge, Higher Education, and the New Managerialism: The Changing Management of UK Universities. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Dyer-Witheford, Nick. 2011. In the Ruined Laboratory of Futuristic Accumulation: Immaterial Labour and the University Crisis. In Cognitive Capitalism, Education and Digital Labor, edited by Michael Peters and Ergin Bulut, 275-286. New York: Peter Lang.
Dyer-Witheford, Nick. 2007. Commonism. Turbulence 1: 81-87. Accessed 11 January 2018. http://turbulence.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2008/07/turbulence_jrnl.pdf
Dyer-Witheford, Nick. 2005. Cognitive Capitalism and the Contested Campus. In Engineering Culture: On the Author as (Digital) Producer, edited by Geoff Cox and Joasia Krysa, 71-93. New York: Autonomedia.
Dyer-Witheford, Nick. 1999. Cyber-Marx: Cycles and Circuits of Struggle in High-Technology Capitalism. Urbana: University of Illinois Press.
Fogle, Calvin and Devonda Elliott. 2013. The Market Value of Online Degrees as a Credible Credential. Global Education Journal (3): 1-25.
Fuchs, Christian. 2008. Internet and Society: Social Theory in the Information Age. New York: Routledge.
Fuchs, Christian and Marisol Sandoval. 2014. Digital Workers of the World Unite! A Framework for Critically Theorising and Analysing Digital Labour. tripleC: Communication, Capitalism & Critique 12 (2): 486-563. Accessed 11 January 2018. http://www.triple-c.at/index.php/tripleC/article/view/549
Fuchs, Christian and Sebastian Sevignani. 2013. What Is Digital Labour? What Is Digital Work? What's Their Difference? And Why Do These Questions Matter for Understanding Social Media? tripleC: Communication, Capitalism & Critique 11 (2): 237-293. Accessed 11 January 2018. http://triple-c.at/index.php/tripleC/article/view/461
Giddens, Anthony. 1981. A Contemporary Critique of Historical Materialism: Volume 1: Power, Property and the State. Berkeley: University of California Press.
Gill, Rosalind. 2014. Academics, Cultural Workers and Critical Labour Studies. Journal of Cultural Economy 7 (1): 12-30.
Gill, Rosalind. 2010. Breaking the Silence: The Hidden Injuries of the Neoliberal University. In Secrecy and Silence in the Research Process: Feminist Reflections, edited by Róisín Ryan-Flood and Rosalind Gill, 228-244. London: Routledge.
Giroux, Henry. 2002. Neoliberalism, Corporate Culture, and the Promise of Higher Education: The University as a Democratic Public Sphere. Harvard Educational Review 72 (4): 425-463.
Gorz, André. 2010. The Immaterial: Knowledge, Value and Capital. London: Seagull Books.
Gregg, Melissa. 2013. Presence Bleed: Performing Professionalism Online. In Theorizing Cultural Work: Labour, Continuity and Change in the Creative Industries, edited by Mark Banks, Rosalind Gill and Stephanie Taylor, 122-134. London: Routledge.
Gulli, Bruno. 2009. Knowledge Production and the Superexploitation of Contingent Academic Labor. Workplace: A Journal for Academic Labor 16: 1-30. Accessed 11 January 2018. http://ices.library.ubc.ca/index.php/workplace/article/view/182232
Hall, Gary. 2008. Digitize This Book! The Politics of New Media, or Why We Need Open Access Now. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press.
Hanley, Larry. 2002. Educational Technology and Academic Labour. Workplace: A Journal for Academic Labor 9: 28-33. Accessed 11 January 2018. http://ices.library.ubc.ca/index.php/workplace/article/view/184044
Hardt, Michael and Antonio Negri. 2009. Commonwealth. Cambridge: Harvard University Press.
Hardt, Michael and Antonio Negri. 2004. Multitude: War and Democracy in the Age of Empire. New York: Penguin Books.
Harris, Kevin. 1982. Teachers and Classes: A Marxist Analysis. London: Routledge.
Harvie, David. 2006. Value Production and Struggle in the Classroom: Teachers within, against and Beyond Capital. Capital & Class 30 (1): 1-32.
Higher Education Funding Council for England. 2009. Enhancing Learning and Teaching through the Use of Technology. Bristol: Higher Education Funding Council for England. Accessed 11 January 2018. http://webarchive.nationalarchives.gov.uk/20120716090505/http://www.hefce.ac.uk/pubs/year/2009/200912/
Higher Education Statistics Agency. 2016. Data and Analysis. Accessed April 6, 2017. Accessed 11 January 2018. https://www.hesa.ac.uk/data-and-analysis
Horkheimer, Max and Theodor Adorno. 1969. Dialektik der Aufklärung: Philosophische Fragmente. Frankfurt am Main: Fischer Verlag.
Jessop, Bob. 2002. The Future of the Capitalist State. Cambridge: Polity Press.
Kinman, Gail and Siobhan Wray. 2013. Higher Stress: A Survey of Stress and Well-Being among Staff in Higher Education. London: University and College Union. Accessed 11 January 2018. https://www.ucu.org.uk/media/5911/Higher-stress-a-survey-of-stress-and-well-being-among-staff-in-higher-education-Jul-13/pdf/HE_stress_report_July_2013.pdf
Krysmanski, Hans-Jürgen. 1990. Produktionsverhältnisse. In Europäische Enzyklopädie zu Philosophie und Wissenschaften. Band 3, edited by Hans Jörg Sandkühler, 894-906. Hamburg: Felix Meiner.
Leisewitz, André. 1990. Produktivkräfte. In Europäische Enzyklopädie zu Philosophie und Wissenschaften: Band 3, edited by Hans Jörg Sandkühler, 914-945. Hamburg: Felix Meiner.
Liesner, Andrea. 2006. Education or Service? Remarks on Teaching and Learning in the Entrepreneurial University. Educational Philosophy and Theory 38 (4): 483-495.
Linardopoulos, Nikolaos. 2012. Employers' Perspectives of Online Education. Campus-Wide Information Systems 29 (3): 189-194.
Lorenz, Chris. 2012. If You're So Smart, Why Are You under Surveillance? Universities, Neoliberalism, and New Public Management. Critical Inquiry 38 (3): 599-629.
Lupton, Deborah. 2014. Digital Sociology. London: Routledge.
Mandel, Ernest. 1992. Introduction. In Capital: A Critique of Political Economy: Volume Two, edited by Karl Marx, 11-79. London: Penguin Books.
Marx, Karl. 1997. Grundrisse: Foundations of the Critique of Political Economy. Accessed April 26, 2013. http://www.marxists.org/archive/marx/works/1857/grundrisse/index.htm
Marx, Karl. 1976. Capital: A Critique of Political Economy: Volume One. London: Penguin Books.
Massy, William and Robert Zemsky. 1995. Using Information Technology to Enhance Academic Productivity. Accessed February 20, 2016. https://net.educause.edu/ir/library/html/nli0004.html
McGettigan, Andrew. 2013. The Great University Gamble: Money, Markets and the Future of Higher Education. London: Pluto Press.
Miller, Henry. 1991. Academics and Their Labour Process. In White-Collar Work: The Non-Manual Labour Process, edited by Chris Smith, David Knights and Hugh Willmott, 109-137. Basingstoke: Macmillan Publishers.
Noble, David. 2001. Digital Diploma Mills: The Automation of Higher Education. New York: Monthly Review Press.
Noble, David. 1998. Digital Diploma Mills: The Automation of Higher Education. First Monday 3 (1). Accessed 11 January 2018. http://journals.uic.edu/ojs/index.php/fm/article/view/569/490
Poritz, Jonathan and Jonathan Rees. 2017. Education Is Not an App: The Future of University Teaching in the Internet Age. London: Routledge.
Pratt, Linda Ray. 1997. Disposable Faculty: Part-Time Exploitation as Management Strategy. In Will Teach for Food: Academic Labor in Crisis, edited by Cary Nelson, 264-277. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press.
Prichard, Craig and Hugh Willmott. 1997. Just How Managed Is the Mcuniversity? Organization Studies 18 (2): 287-316.
Rosa, Hartmut. 2013. Social Acceleration: A New Theory of Modernity. New York: Columbia University Press.
Ross, Andrew. 2009. Nice Work If You Can Get It: Life and Labor in Precarious Times. New York: New York University Press.
Ross, Andrew. 2000. The Mental Labor Problem. Social Text 18 (2): 1-31.
Sandoval, Marisol. 2014. From Corporate to Social Media: Critical Perspectives on Corporate Social Responsibility in Media and Communication Industries. London: Routledge.
Sandoval, Marisol. 2013. Foxconned Labour as the Dark Side of the Information Age: Working Conditions at Apple's Contract Manufacturers in China. tripleC: Communication, Capitalism & Critique 11 (2): 318-347. Accessed 11 January 2018. http://triple-c.at/index.php/tripleC/article/view/481
Shumar, Wesley. 1995. Higher Education and the State: The Irony of Fordism in American Universities. In Academic Work: The Changing Labour Process in Higher Education, edited by John Smyth, 84-98. Buckingham: Society for Research in Higher Education & Open University Press.
Tancred-Sheriff, Peta. 1985. Craft, Hierarchy and Bureaucracy: Modes of Control of the Academic Labour Process. Canadian Journal of Sociology 10 (4): 369-390.
Terranova, Tiziana and Marc Bousquet. 2004. Recomposing the University. Mute, July 13. Accessed 11 January 2018. http://www.metamute.org/editorial/articles/recomposing-university
Tirelli, Vincent. 1999. Adjuncts and More Adjuncts: Labor Segmentation and the Transformation of Higher Education. In Chalk Lines: The Politics of Work in the Managed University, edited by Randy Martin, 181-201. Durham: Duke University Press.
University and College Union. 2016a. Workload Is an Education Issue: UCU Workload Survey Report 2016. London: University and College Union. Accessed 11 January 2018. https://www.ucu.org.uk/media/8195/Workload-is-an-education-issue-UCU-workload-survey-report-2016/pdf/ucu_workloadsurvey_fullreport_jun16.pdf
University and College Union. 2016b. HE Rate for the Job. Accessed April 21, 2016. https://www.ucu.org.uk/article/8087/HE-rate-for-the-job
University and College Union. 2016c. When Is a Pay Rise Not a Pay Rise? Accessed April 21, 2016. https://www.ucu.org.uk/when-is-a-pay-rise-not-a-pay-rise?utm_source=campaignupdate._all-members&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=lyr-UCU+campaigns+update:+18+March+2016&utm_term=SC004
University and College Union. 2014. UCU Survey of Work-Related Stress. London: University and College Union. Accessed 11 January 2018. https://www.ucu.org.uk/media/6908/UCU-survey-of-work-related-stress-2014---summary-of-findings-Nov-14/pdf/ucu_stresssurvey14_summary.pdf
University of Edinburgh. 2016. What Is Online Learning? Accessed July 19, 2017. http://www.ed.ac.uk/studying/postgraduate/degree-guide/online-learning/about
van Dyk, Silke and Tilman Reitz. 2016. Projektförmige Polis und akademische Prekarität im universitären Feudalsystem (Teil 1). SozBlog. Blog der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Soziologie, June 9. Accessed 11 January 2018. http://soziologie.de/blog/2016/06/projektfoermige-polis-und-refeudalisierung
van Mourik Broekman, Pauline, Gary Hall, Ted Byfield, Shaun Hides and Simon Worthington. 2015. Open Education: A Study in Disruption. London: Rowman & Littlefield Publishers.
Watts, Jenny and Noelle Robertson. 2011. Burnout in University Teaching Staff: A Systematic Literature Review. Educational Research 53 (1): 33-50.
Werry, Chris. 2002. The Rhetoric of Commercial Online Education. Workplace: A Journal for Academic Labor 9: 34-44. Accessed 11 January 2018. http://ices.library.ubc.ca/index.php/workplace/article/view/184045
Willmott, Hugh. 1995. Managing the Academics: Commodification and Control in the Development of University Education in the UK. Human Relations 48 (9): 993-1027.
Winn, Joss. 2015. Writing About Academic Labour. Workplace: A Journal for Academic Labor 25: 1-15. Accessed 11 January 2018. http://ices.library.ubc.ca/index.php/workplace/article/view/185095
Winn, Joss. 2012. Open Education: From the Freedom of Things to the Freedom of People. In Towards Teaching in Public: Reshaping the Modern University, edited by Mike Neary, Howard Stevenson and Les Bell, 133-147. London: Continuum.
Wright, Erik Olin. 2010. Envisioning Real Utopias. London: Verso Books.
Wright, Erik Olin. 1997. Class Counts: Comparative Studies in Class Analysis. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Wright, Erik Olin. 1978. Class, Crisis and the State. London: Verso Books.
Wright, Steve. 2002. Storming Heaven: Class Composition and Struggle in Italian Autonomist Marxism. London: Pluto Press.
About the Author
Thomas Allmer
Thomas Allmer is Lecturer in Digital Media at the University of Stirling, Scotland, UK, and a member of the Unified Theory of Information Research Group, Austria. His publications include Towards a Critical Theory of Surveillance in Informational Capitalism (Peter Lang, 2012) and Critical Theory and Social Media: Between Emancipation and Commodification (Routledge, 2015). For further information, please see: http://allmer.uti.at